Abstract
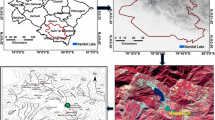
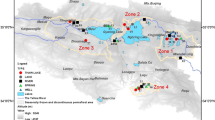
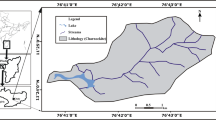
Exchange of water between groundwater and surface water could alter water quality of the surface waters and thereby impact its ecosystem. Discharges of anoxic groundwater, with high concentrations of sulfate and chloride and low concentrations of nitrate and oxygen, from three sinkhole vents (El Cajon, Middle Island and Isolated) in Lake Huron have been recently documented. In this investigation, we collected and analyzed a suite of water samples from these three sinkhole vents and lake water samples from Lake Huron for Ra, radon-222, stable isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen, and other ancillary parameters. These measurements are among the first of their kind in this unique environment. The activities of Ra are found to be one to two orders of magnitude higher than that of the lake water. Isotopic signatures of some of the bottom lake water samples indicate evidences for micro-seeps at distances farther from these three vents. A plot of δD versus δ18O indicates that there are deviations from the Global Meteoric Line that can be attributed to mixing of different water masses and/or due to some subsurface chemical reactions. Using the Ra isotopic ratios, we estimated the transit times of the vent waters from the bottom to the top of the vent (i.e., sediment–water interface) to be 4–37 days. More systematic studies on the distribution of the radioactive and stable isotope studies are needed to evaluate the prevalence of micro-seeps in Lake Huron and other Great Lakes system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Baskaran M, Murphy DJ, Santschi PH, Orr JC, Schink DR (1993) A method for rapid in situ extraction and laboratory determination of Th, Pb and Ra isotopes from large volumes of seawater. Deep-Sea Res 40(4):849–865
Biddanda BA, Coleman DF, Johengen TH (2006) Exploration of a submerged sinkhole ecosystem in Lake Huron. Ecosystems 9:828–842
Biddanda BA, Nold SC, Ruberg SA, Kendall ST, Sanders TG, Gray JJ (2009) Submerged sinkhole ecosystems in the Laurentian Great Lakes: a microbiogeochemical frontier. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 90:61–62. doi:10.1029/2009EO080001
Biddanda B, Nold S, Dick G, Kendall S, Vail J, Ruberg S, Green C (2012) Rock, water, microbes: sinkholes in Lake Huron are habitats for ancient microbial life. Nat Educ Knowl 3(3):13
Burnett WC, Aggarwal PK, Aureli A (2006) Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. Sci Total Environ 367:498–543
Cable J, Bugna G, Burnett WC, Chanton J (1996) Application of 222Rn and CH4 for assessment of groundwater discharge to the coastal ocean. Limnol Oceanogr 41:1347–1353
Church TM (1996) An underground route for the water cycle. Nature 380:579–580
Coleman DF (2002) Underwater archaeology in Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary, Lake Huron. Mar Technol Soc J 36(3):33–44
Daansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Davis CO, Simmons MS (1979) Water chemistry and phytoplankton field and laboratory procedures. Special report no. 70. Great Lakes Research Division, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Domack E, Ishman S, Leventer A (2005) A chemotrophic ecosystem beneath Antarctic Ice Shelf. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 86:269–276
Dymond J, Collier RW, Watwood ME (1989) Bacterial mats from Crater Lake Oregon and their relationship to possible deep-lake hydrothermal venting. Nature 342:673–675
Etemad-Shahidi A, Imberger J (2006) Diapcynal mixing in the thermocline of Lakes: estimates by different methods. Environ Fluid Mech 6:227–240
Gardner WC (1974) Middle Devonian stratigraphy and depositional environments in the Michigan Basin. Michigan Basin Geological Society, Grand Ledge
Grannemann NG, Hunt RJ, Nicholas JR, Reilly TE, Winter TC (2000). The importance of groundwater in the Great Lakes region. In: USGS water resources investigations report 00-4008. USGS, Lansing
Hagerthey SE, Kerfoot WC (1998) Groundwater flow influences the biomass and nutrient ratios of epibenthic algae in a north temperate seepage lake. Limnol Oceanogr 43(6):1227–1242
Hammond DE, Zukin JG, Ku TL (1988) The kinetics of radioisotope exchange between brine and rock in a geothermal system. J Geophys Res 93:13175–13186
Hebting Y, Schaeffer P, Behrens A (2006) Biomarker evidence for a major preservation pathway of sedimentary organic carbon. Science 312:1627–1631
Herczeg AL, Simpson HJ, Anderson RF, Trier RM, Mathieu GG, Deck BL (1988) Uranium and radium mobility in groundwaters and brines within the Delaware basin, south-eastern New Mexico, U.S.A. Isot Geosci 8:181–196
Johengen TH, Nalepa TF, Fahnenstiel GL et al (1995) Nutrient changes in Saginawa Bay, Lake Huron, after the establishment of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). J Great Lakes Res 21:449–464
Jweda J, Baskaran M, van Hees E, Schweitzer L (2008) Short-lived radionuclides (7Be and 210Pb) as tracers of particle dynamics in a river system in southeast Michigan. Limnol Oceanogr 53(5):1934–1944
Key RM, Brewer RL, Stockwell JH, Guinasso NL Jr, Schink DR (1979) Some improved techniques for measuring 222Rn and 226Ra in marine sediments and in seawater. Mar Chem 7:251–264
Kraemer TF (2005) Radium isotopes in Cayuga Lake, New York: indicators of inflow and mixing processes. Limnol Oceanogr 50(1):158–168
Kraemer TF, Curwick PB (1991) Radium isotopes in the lower Mississippi River. J Geophys Res 96(C2):2797–2806
Krishnaswami S, Graustein WC, Turekian KK, Dowd JW (1982) Radium, thorium, and radioactive lead isotopes in Groundwaters: application to the in situ determination of adsorption–desorption rate constants and retardation factors. Water Resour Res 18:1633–1675
Krishnaswami S, Bhushan R, Baskaran M (1991) Radium Isotopes and 222Rn in Shallow Brines, Kharagoda (India). Chem Geol (Isot Geosci Sect) 87:125–136
Langmuir D, Reise AC (1985) The thermodynamic properties of radium. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49:1593–1601
Long DT, Wilson TP, Takacs MJ, Rezabek DH (1988) Stable-isotope geochemistry of saline near-surface groundwater: east-central Michigan basin. Geol Soc Am Bull 100:1568–1577
Mathieu GG, Biscay PE, Lupton RA, Hammond DE (1988) System for measurement of 222Rn at low levels in natural waters. Health Phys 55:989–992
McIntosh JC, Walter LM (2006) Paleowaters in Silurian–Devonian carbonate aquifers: geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Great Lakes region since the Late Pleistocene. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(10):2454–2479
Menzel DW, Corwin N (1965) The measurement of total phosphorus liberated in seawater based on the liberation of organically bound fractions by persulfate oxidation. Limnol Oceanogr 10:280–281
Michael HA, Mulligan AE, Harvey CF (2005) Seasonal oscillations in water exchange between aquifers and the coastal ocean. Nature. doi:10.1038/nature03935
Moore WS (1996) Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments. Nature 380:612–614
Nold SC, Zajack HA, Biddanda BA (2010) Archaeal and Eukaryal diversity in a submerged sinkhole ecosystem influenced by sulfur-rich, hypoxic groundwater. J Great Lakes Res 36:366–375
Nold SC, Bellecourt MJ, Kendall ST et al (2013) Underwater sinkhole sediments sequester Lake Huron’s carbon. Biogeochemistry 115:235–250
Raidla V, Kirsimae K, Vaikmae R et al (2011) Geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Cambrian–Vendian aquifer system of the Baltic Basin. Chem Geol 258:219–231
Ruberg SA, Coleman DE, Johengen TH (2005) Groundwater plume mapping in a submerged sinkhole in Lake Huron. Mar Technol Soc J 39:65–69
Ruberg SA, Kendall ST, Biddanda BA, Black T, Lusardi W, Green R, Casserley T, Smith E, Nold S, Sanders TG, Lang G, Constant S (2008) Observations of the Middle Island sinkhole in Lake Huron: a unique hydrologic and glacial creation of 400 million years. Mar Technol Soc J 42(4):12–21
Todd JF, Elsinger RJ, Moore WS (1988) The distributions of uranium, radium, and thorium isotopes in two anoxic fjords: Framvaren Fjord (Norway) and Saanich Inlt (British Columbia). Mar Chem 23:393–415
Turekian KK, Cochran JK (1986) Flow rates and reaction rates in the Galapagos Rise spreading center hydrothermal system as inferred from 228Ra/226Ra in vesicomyid clam shells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83:6241–6244
Yurtsever Y, Gat JR (1981) Atmospheric waters. In: Gat JR, Gonfiantini R (eds) Stable isotope hydrology, deuterium and oxygen-18 in the water cycle. International Atomic Energy Agency Technical Report 210, pp 103–142
Zhang L, Zhang J, Swarzenski PW, Liu Z (2011) Radium isotope tracers to evaluate coastal ocean mixing and residence times. In: Baskaran M (ed) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry. Springer, Berlin, pp 331–343
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support for dive operations by Russ Green, Jeff Gray, Tane Casserley, Wayne Lusardi, and Joe Hoyt of the Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary. We thank Dennis Donahue, Steve Bawks, Beau Braymer, Mike Taetsch, Tom Joyce, Andrew Yagiela, Jack Workman, and Rob Paddock for vessel and ROV operations, Scott Kendall for some chemical analysis and Cathy Darnell (NOAA-Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory) for help in preparing a figure. This work was supported by the NOAA Ocean Exploration Program (subcontract to Wayne State University via CILER), the NOAA National Undersea Research Center at the University of Connecticut at Avery Point and the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, NOAA-GLERL and Cooperative Institute for Limnology and Ecosystem Research (CILER). This is GLERL contribution #1805. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their thorough and thoughtful reviews which helped to improve this manuscript. The first author acknowledges the long-term scientific collaboration and friendship with Tom Church to whom this special volume is dedicated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baskaran, M., Novell, T., Nash, K. et al. Tracing the Seepage of Subsurface Sinkhole Vent Waters into Lake Huron Using Radium and Stable Isotopes of Oxygen and Hydrogen. Aquat Geochem 22, 349–374 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-015-9286-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-015-9286-7